

北京博普特科技有限公司成立于2008年,是一家专注于研发、生产、系统集成、销售技术服务一体化的高科技公司。公司主要为植物、食品、生态、环境行业提供科研仪器以及系统解决方案,公司运营团队拥有丰富仪器行业经验以及化视野,技术和销售团队由专业博士和硕士组成,工程师团队拥有多年售后维修经验。

04.14
2025
04.14
2025
03.03
2025
02.21
2025

北京博普特科技有限公司
服务尽善尽美,技术精益求精




HAIP带RGB通路高光谱成像系统
HAIP高端带RGB通路高光谱成像...

WIWAM植物表型成像分析系统conveyor
WIWAM conveyor是一款...

多光谱植物表型特征分析Videometer数据分析
该系统可通过较优化的方式实现植物样...

计算机断层扫描技术-微型CT植物CT
微型CT系统不仅利用在如生物学,如...

植物表型成像系统
WIWAM Screen植物表型...
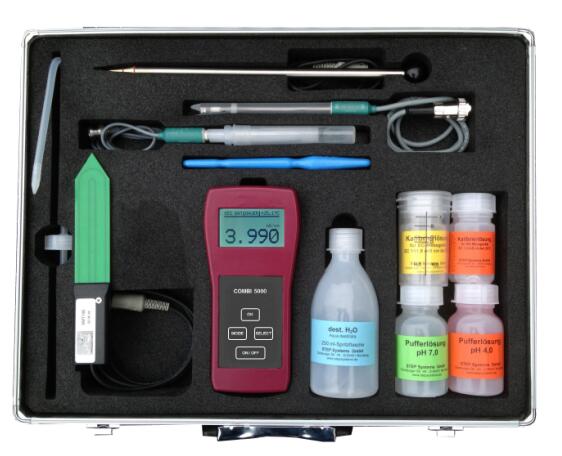
土壤多参数速测仪分析仪Combi5000
COMBI 5000分析仪可对较重...

Aquation叶绿素荧光自动监测仪
叶绿素荧光技术广泛应用于植物光合作...
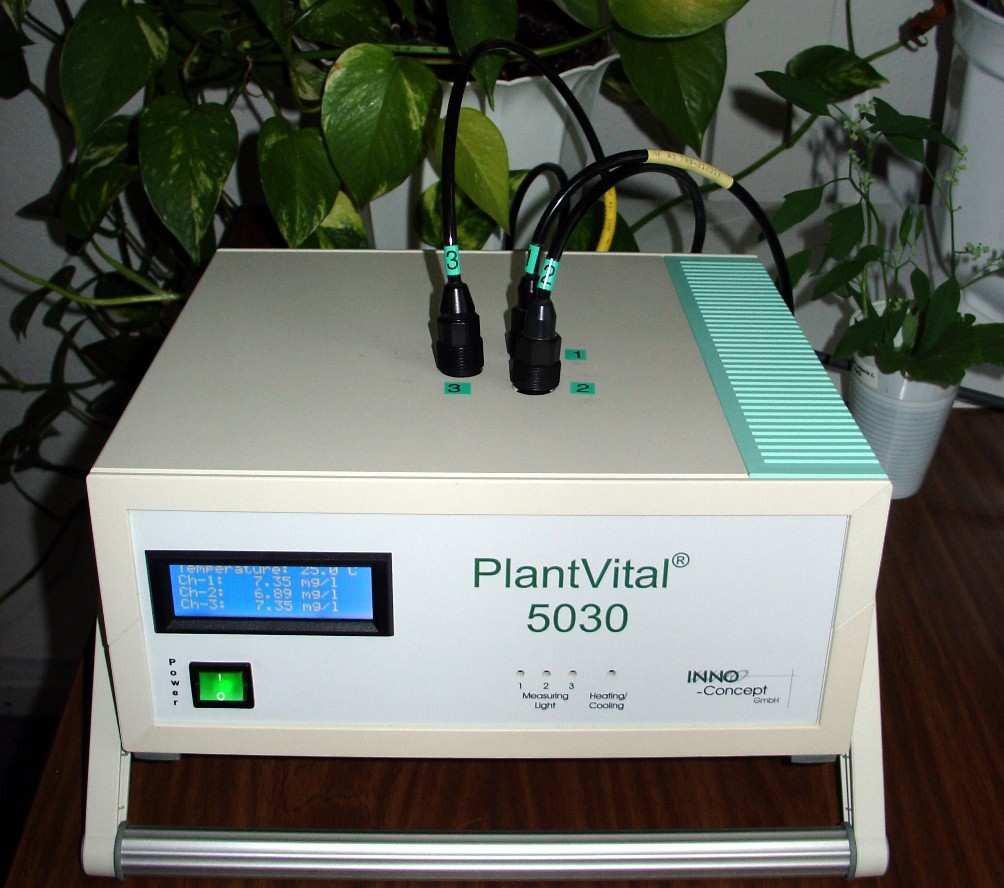

植物生长监测系统
STEP-PTM-50植物在线光合...

高通量植物逆境生物学研究系统
Plantarray广泛应用于生物...
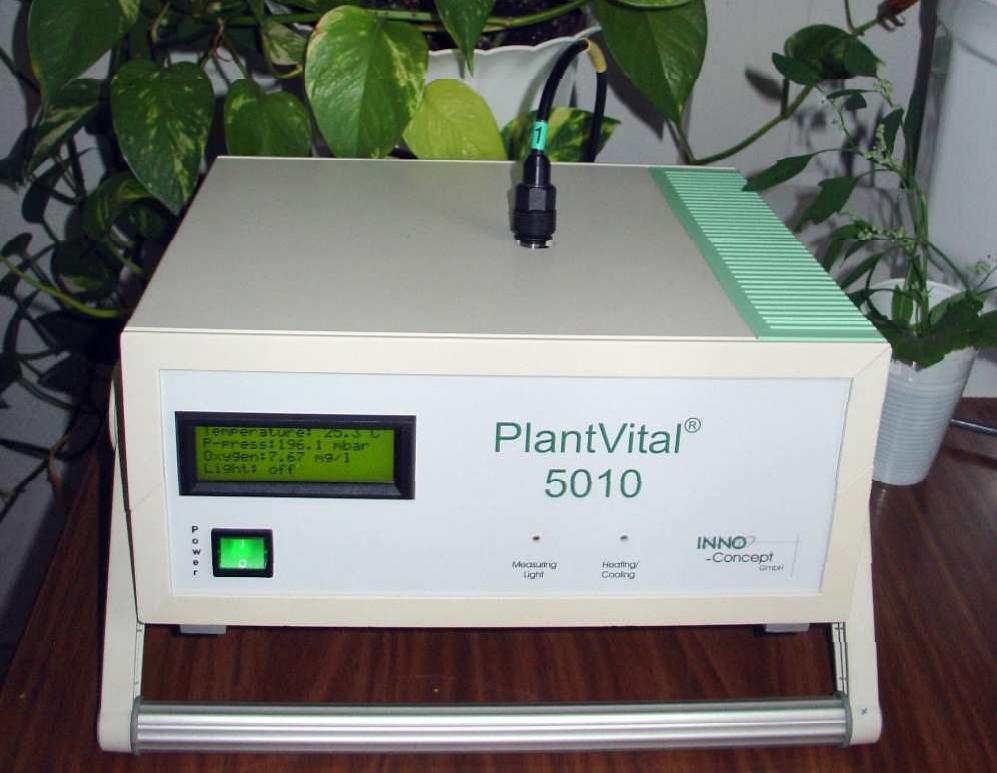

德国STEPS植物生理生态监测系统
STEP-PTM-50植物在线光合...

Videometer Lite多光谱植物病理表型成像系统
便携式乙烯测试仪MACView提供...

北京博普特科技有限公司
专注品质,用心为您服务



